Melanoma is one of common and dangerous types of skin cancer; it may be fatal if not treated at an early stage. Melanomas are usually similar to moles, and sometimes are caused by moles. They are mostly black and brown, but they can be pink, red, blue or even white. Although it can develop anywhere on the skin, it is seen more intensely in the chest and back in males and in the legs in females. They may also develop in the neck, face, eye, mouth, genital area or even in the anal region. Factors such as exposure to harmful rays of the sun, solarium and light skin color, although mostly genetic, also trigger melanoma. Symptoms are asymmetric, unclear, pink, blue, moles or lesions that can be of different colors. In the treatment of early melanoma, surgical intervention is generally used and tumor tissues are removed; the success rate is very high.
Table of Contents
What is melanoma?
Melanoma is dangerous types of skin cancer and easily spread to other organs. It usually starts in a skin cell and the most common cause of death, even if it is not common among skin cancers. Melanoma, also called malignant melanoma or cutaneous melanoma, begins in melanocytes. Melanocytes are the cells producing melanin, which can be turned into melanoma in following process and gives color to the skin, is the cells that make brown pigments. Melanocytes are located in the epidermis, the upper layer of the skin.
In addition to giving the skin its brown color, the melanin protect the lower layers of the skin against harmful effects of the sun. When skin is exposed to sun for a long time, melanocytes produce more amounts of melanin and skin becomes tanned and darkened.
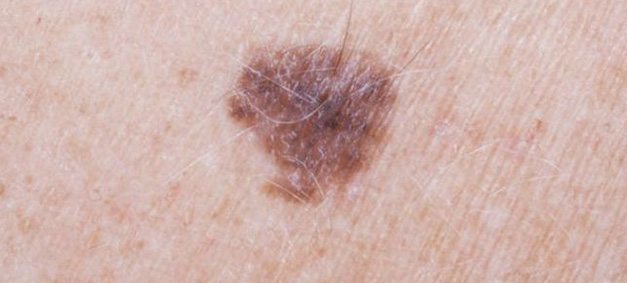
Since melanoma cells continue to produce melanin, melanoma tumors are brown or black in many patients. In cancer patients whose melanin production stopped, tumors may be pink, brown or even white.
Causes of melanoma
- The main cause of melanoma is abnormal melanocyte skin cells
- Malignant melanoma usually develops from moles (nevus).
- Long-term exposure to UVA and UVB rays during sunbathing or solarium
- Non-normal (atypical) moles found in the skin
- Having fair eye and skin color and a sensitive skin type
- Have previously had melanoma
- The weakening of the immune system due to organ transplants, chemotherapy, AIDS, lymphoma
- Having a melanoma in a family history
Symptoms of melanoma
- Asymmetry: The moles in the skin are asymmetric and they are not alike.
- Boundary: The boundaries of moles are unclear, edges are scalloped and notched.
- Color: Melanoma can be red, white, pink, black, skin color or brown.
- Diameter: Size of moles, diameter is large. It is usually more than 6 mm
- Expansion: Cancerous moles expand and grow.
The moles in the skin are usually harmless. Symptoms are usually seen in one or two moles in the early stages, quite different from the other ones. To distinguish these symptoms ABCDE (Asymmetry, Border, Color, Diameter and Evolving) rule is used.
When there is enlargement, size, shape, discoloration, bleeding, itching, crusting, consult a doctor immediately.
Melanoma types
Melanoma is divided into different groups according to the shape and characteristics of the moles.
Melanoma spreading on the surface
It is more common in people with freckled and pale skin. The moles usually grow outward and their borders are irregular. When they go down to the deeper layers of the body, they have the risk of spreading to other organs.
Nodular melanoma
They grow very quickly and can even go down to the lowest layers of the skin. Melanomas, which may be red, grow on normal skin. They are mostly seen in the head, neck, back and chest. They are evident by bleeding and leakage.
Lentigo malignant melanoma
It is one of 10 cases of melanoma. It is mostly seen in the elderly who are very exposed to the sun. They are larger and darker than the freckles. At first, the flat moles can gradually grow and change over time. Over the years, they can form the nodules by growing down to the lower layer of the skin.
Acral lentigous melanoma
A rare form of melanoma seen on the hands and feet. Sometimes they can develop around the nail. Although it is more common in dark-skinned people, it can also be seen in fair skinned or haired people.
Amelanotic melanoma
In this rare melanoma, moles may be pink, red, gray, brown, sometimes colorless.
Melanoma cancer stages
The stage of a cancer expresses how far the cancer has spread. Doctors plan the treatment process according to the stage of cancer. The stages of melanoma are between 0-4.
- In stage 0, cancer is only in the outermost layer of the skin and is generally non-hazardous.
- In stage 1, the tumor is thinner than 2 mm, and may be ulcerated or non-ulcerated.
- Although cancer cells that may be ulcerated or non-ulcerated in stage 2 may be thicker than 4 mm, they have not yet spread to surrounding tissues.
- In Stage 3, the cancer that spreads to the surrounding tissues does not spread to distant tissues and organs.
- In the 4th most dangerous phase, the cancer spread to nearby lymph nodes and spread to very important distant organs such as the lung, liver and brain.
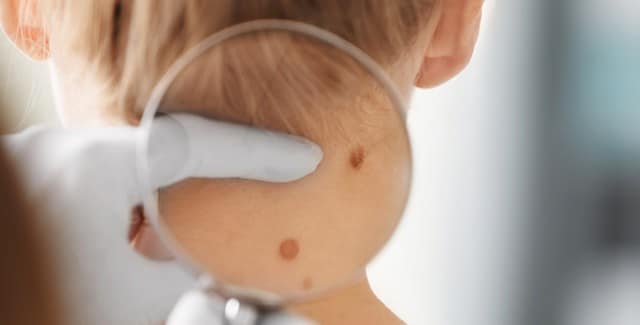
Diagnosis of melanoma cancer
For diagnosis of melanoma, firstly, you are asked about your medical history and moles in your skin are examined. If there is a suspicious condition, a biopsy is performed. The mole removed by a surgical intervention, and is examined closely to find whether it is melanoma. In addition, it can be checked whether the melanoma is spread to nearby tissues by the Sentinal node biopsy.
Shave (tangential) biopsy, punch biopsy, Incisional and excisional biopsies reflectance confocal microscopy, sentinel lymph node biopsy are among the types of biopsies frequently used in the diagnosis of melanoma. Melanoma tisues that taken by biopsy sends to pathologist for diagnosis. Pathology reports of melanoma will include a description of tumour thickness, which can be expressed as Clark level or Breslow thickness. Clark level is a decrete measure indicative of the anatomical level of invasion.
Treatment of malignant melanoma cancer
Treatment of the disease usually depends on the stage of the melanoma. In cases where melanoma is diagnosed early, fatal consequences that caused by cancer can be prevented. Surgical intervention is usually preferred in the treatment of early cancer. In advanced stages, drugs that inhibit the spread of cancer cells, such as BRAF inhibitors, can be prescribed.
Malignant melanoma surgery
In most cases, thin melanomas are removed under local anesthesia. Postoperative small scars will heal spontaneously over time. The surgical excision is used to treat all skin cancer types. Although the wounds usually heal 1-2 weeks after the procedure, this period depends on the patient completing the wound care completely.
Microscopic surgery
Recently, as an alternative to excision, microscopic surgery is a preferred method. With this method, a thin tissue is removed from the melanoma and cancer cells are examined under a microscope. The removal of the tissues continues until all cancerous cells are completely removed. The method is different from other surgical methods because it shows how deep the cancer cells are.
Immunotherapy for treatment of melanoma
New therapies (as immunotherapy) have been increased survival rates. It is the first time, there’s a treatment for melanoma with immunotherapy but these drugs don’t work on the all melanoma patients. Immunotherapy can be used in the 3rd and 4th stages of melanoma cancer, in which cancer cells progress deeply or spread to distant organs. Drugs injected intravenously into the patient can significantly extend the patient’s life expectancy. In last a few years, many new drugs aprroved for treatment of melanoma include ipilimumab (Yervoy), nivolumab (Opdivo) and pembrolizumab (Keytruda).
Targeted treatments
With targeted therapies, certain cancer cells in stage 3 and 4 are identified and these cells that are effective in the spread of cancer are blocked.
The drugs used are vemurafenib, dabrafenib and trametinib.
Side effects of targeted therapies are variable. Skin problems, fever, chills and dehydration can be seen.
Chemotherapy
Today, although targeted therapy and immunotherapy are more used in the treatment of melanoma, chemotherapy may also be used in the treatment of the 3rd and 4th stage melanoma in addition to these therapies.
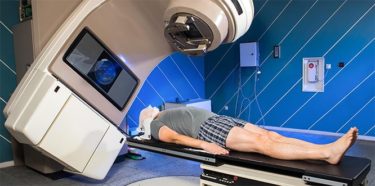
Radiation therapy
As with other types of skin cancer, radiation therapy may be necessary in addition to chemotherapy drugs for advanced melanoma treatment. High-energy X-rays with external beam radiation therapy focus on tumors in the epidermis layer of the body. With radiation therapy used in the treatment of the 3rd and 4th stage melanoma, the spread of melanoma to the brain and the growth of the tumor can be stopped.
Will Melanoma kill you? Malignant melanoma survival
Early stage melanoma, which has not reached the 3rd and 4th stages, can often be treated. However, risk of death is high in patients with 3th and 4th advanced melanoma.
Although life expectancy of the 4th stage patients is extended by non-surgical methods for a few months and sometimes for a few years, it is unfortunately not possible to get rid of the disease completely. Therefore, early diagnosis of the disease is extremely important.
Metastatic melanoma
Melanoma tumors, may spreads to others organs especialy in the late stages (stage-III or stage-IV) and calls as metastatic melanoma. When it spreads to lungs is called metastatic melanoma of the lung (melanoma with lung metastases). Melanoma often spreads to; tissue under the skin, brain, lungs, lymph nodes and liver. Metastatic melanoma can’t be cured, but treatments and support can help you live longer and better.
Symptoms of metastatic melanoma
- Bone pain
- Weight loss
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Seizures
- Shortness of breath or cough
- Swelling of the liver
- Headaches
Herbal treatment of melanoma
Some plants can be used to prevent the spread of cancer cells or to prevent cancer in the early stage of skin cancer. These treatments, however, cannot replace surgical treatment or medication in any way. Always consult your doctor before you try herbal treatment methods.
You can find information about the herbs in the treatment of melanoma and skin cancer below yet, the scientific basis of some of this information is limited!
Turmeric
You can benefit from the natural treatment of melanoma from turmeric, which prevents the spread of cancer cells to larger areas. You can consume one teaspoon of turmeric a day with yogurt or drink a cup of turmeric tea.
Green tea
A strong antioxidant and antibacterial green tea destroys cancerous cells. The regular consumption of 2-3 cups of green tea every day is protective against not only skin cancer but also many cancer.
Garlic
As an excellent natural antibiotic, garlic strengthens the immune system and prevents cancer. By consuming a few cloves of raw garlic a day, you can be protected from melanoma.
Red beet
You can fight melanoma by adding red beet to your nutrition program which contains substances that prevent the spread of cancer in its components. Red beet can be consumed by raw or squeezing water.
Green leafy vegetables
You can reduce your risk of getting melanoma by eating lycopene-containing foods frequently such as tomato, as well as green leafy vegetables such as spinach, leek, which help the body to fight the cancer cells by strengthening the immune system, which also significantly increase the body’s beta-carotene needs.
Skin cancer and melanoma protection methods
- Periodically check the moles in your skin.
- Be careful not to go out between hours 10:00-16:00, especially when the UV rays are the most harmful in summer months.
- Make sure that the sun protection creams you use protect against UVB and UVA rays.
- If you have a light skin color, blond hair, red hair and you are freckled; use sun protection creams with a protection factor of at least 30%.
- Apply sun protection cream to your skin at least 30 minutes before you go out.
- Use sun protection cream even when you are in your home, in car or at shade. Note that UVB rays may even penetrate through the windows.
- Apply sun protection creams in every two hours.
- Avoid sunbathing on deckchairs, especially if you have a skin that is pale, thin and skin has too much moles
Melanoma in childhood
Although the likelihood of melanoma in children is extremely low, it is not impossible. Melanoma is the second most common cause of skin cancer in children. Children with sunburn, especially on skin, are at risk.
Precautions we can take to protect children:
- Apply sun protection creams having +15 more protection percentage to children before sun exposure.
- Do not expose babies between 0-6 months to direct sunlight.
- Cover car windows with UV films
- Use a stroller with sun protection.
- Do not take your baby out between 10 am and 4 pm.
Recommendations for patients with melanoma cancer
- Never lose your hope and keep your morale at high level.
- Do not neglect a regular and balanced diet in any way.
- Get plenty of rest during treatment.
- Get psychological support if you feel unhappy, depressed and sensitive.
- Go to chemotherapy and radiotherapy sessions on time.
- Always have good communication with your doctor and nurse.
- Spend a lot of time with your loved ones to keep your mood high.
- Inform your doctor about all prescription medications you use before starting treatment. For more: >>> Melanoma