Antiseptics are antimicrobial chemicals applied to the skin or mucous membrane to prevent infection. Today, it is frequently used both in medical settings and daily life. They preventing the proliferation and spread of germs should not be confused with disinfectants with a fatal effect on microorganisms. With multiple ways of use, antiseptics are available on the market as solutions, gel, or cream. Baticon, alcohol and hydrogene peroxide are the most commonly used antiseptics; they are indispensible parts of surgical and first aid interventions.
Table of Contents
What is antiseptic?
Antiseptic is a chemical substance which stops or slows the proliferations of harmful microorganisms without killing them. It is often used to reduce the risk of infection, especially during surgery and other medical interventions. Different types are used in medical settings.
For example, surgeons wash their hands and arms with antiseptics before a surgery, thereby minimizing the risk of infection which may occur during a surgery. The most commonly used types are alcohol, baticon and hydrogen peroxide.
What is a disinfectant?
Disinfectants are used to kill or eliminate microorganisms. Another area of use is to neutralize viruses and germs on fomites and surfaces (medical devices, equipments, wall, ground etc.). Exposure of the skin or living surfaces to disinfectants made of strong chemicals should be avoided; temporal or permanent damage may occur.
Differences between antiseptic and disinfectant
It is not true that they are similar products. The biggest difference is that antiseptics are applied to the skin and living surfaces; however, disinfectants are used on fomites and equipments. Exposure of the skin to disinfectants should definitely be avoided.
For example, a surgeon uses an antiseptic to clean the area of intervention during a surgery. However, s/he uses a disinfectant to sanitize an operation table. (1)
Both of them contain a chemical called biocide. It is a chemical helping prevent microorganisms at lower concentrations and eliminate them at higher concentration
The role of antiseptics
They are applied to the skin and mucous membrane where germs are present in high density. (2)
How to use antiseptics?
There are many different ways of use of them in medical settings and other enviroments. For example:
- Washing hands: Hand and body hygiene with antiseptic wash products, also known as antibacterial soaps. However, it is advised to use natural soap and water for hand and body hygiene. (3)
- Scrubbing: Sanitization of hands and arms before every surgical procedure especially by those working at medical settings. Use of antiseptic wipes and hand sanitizer gels can be included in this way of use. These products are for use when there is no soap and water; they cannot be rinsed with water. (4)
Antiseptic wipes and hand disinfectants should be stored out of the reach of children and used only as instructed by the product label.
- Disinfecting the skin mucosa: Applying an antiseptic to urethra, bladder or vagina before procedures such as catheter insertion. In this method, both infections with which a catheter may become infected are prevented and a treatment is administered by means of the use of an antiseptic if there is an infection.
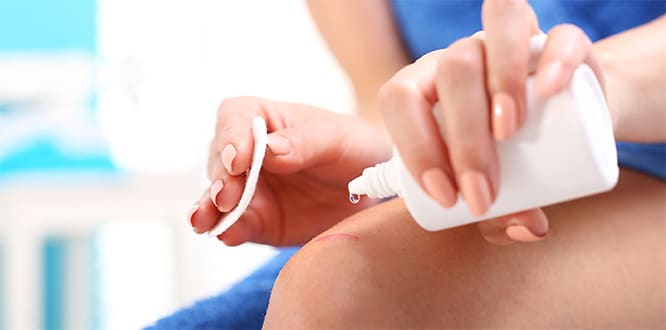
- Treatment of the skin infections: Damaged sites are disinfected with an antiseptic to prevent infections which may develop due to minor cuts, superficial burns and wounds.
- Treatment of mouth and throat infections: Many medical throat lozenges contain antiseptics. They help reduce sore throat caused by bacterial infection. Moreover, antiseptic drugs can be taken in the treatment of mouth sores and aphtae.
Safe use of antiseptics
- They are chemical substances and the structure of each chemical is not compatible with each other. Therefore, it may be dangerous for anybody who has no expertise on them to combine antiseptics or take one after another. One specific type should be determined to apply to the wound to be treated and only that should be used.
- Specific types should be applied to different types of wound. For example:
- Open wounds should be disinfected with antiseptics not containing alcohol, thereby preventing skin burn.
- Antiseptics penetrating through the skin are preferred for closed or superficial wounds.
- For wounds due to soil, pebbles, stone, rock etc., solutions providing thorough disinfection without irritation.
- Burns should be cleansed using solutions with high water density. This helps prevent possible fungal infection and alleviate burning sensation.
Consult your doctor if you need to use an antiseptic for situations other than superficial wounds.
What are the factors to consider when using an antiseptic?
The concentration of biocide in antiseptics is critical. The antiseptic that you use should not damage the skin, body tissue, and body cells while preventing the proliferation of microorganisms.
After uncovering the container, antiseptics should be used for up to 2 weeks, while those containing alcohol should be used for up to 1 month. They should be kept away from other medicines and stored out of the reach of children.
When to use antiseptics?
They should be applied to the sites and wounds with the risk of infection. Unnecessary use may cause skin damage.
Types and forms of antiseptics
Antiseptic solutions
They are liquid used to cleanse wounds. They help cleanse and disinfect wounds. The most commonly used solutions are:
- Povidone-iodine: Povidone-iodine is the most preferred solution with its wide area of use. It is especially used for small wounds during first-aid. It is also used to disinfect the skin and mucosa during in gynecological interventions and surgical procedures. Baticonol scrub is a surgical hand sanitizer. (5)
- Ethyl alcohol: 70% ethyl alcohol can be used. If used properly, it can eliminate the bacteria on the skin surface up to 90% within two minutes. Its use on open wounds and mucosa is dangerous due to alcohol content. (6)
- Oxygenated water: Oxygenated water is commonly used to cleanse wounds. It can also be used as a mouthwash and throat antiseptic.
Antiseptic creams
Inflammations, infections and edema on the skin surface are treated with the help of antiseptic creams. These creams can be used to treat deep cuts, surgical wounds and burns. Moreover, they help the skin tissue regenerate quickly and reduce damage and pain of the area burnt.
They can be applied to any part of the skin, except the eyes and mouth. An antiseptic cream is applied to the site and the skin is allowed to absorb the cream by rubbing. If they are used for open wounds such as surgical wounds, deep cuts, the site should be covered with a gauze after applying the cream to the tissue. The skin should be cleaned with water before applying the cream again.
What is Antiseptic Resistance?
Microorganisms have a high level of ability to adapt themselves to different conditions. For example, microorganisms that remain in antiseptic solutions for a long time may develop resistance. In addition, insufficient and incorrent use of an antiseptic may increase this resistance.
Side effects and harms of antiseptics
Alcoholic antiseptics are absorbed by the skin. Therefore, when used incorrectly, they may cause damage to the skin surface, eye surface, upper respiratory tract and trachea. If povidone-iodine is used incorrectly, though rare, or if an allergic reaction develops, it may cause serious skin damage, burns, cough and dizziness.