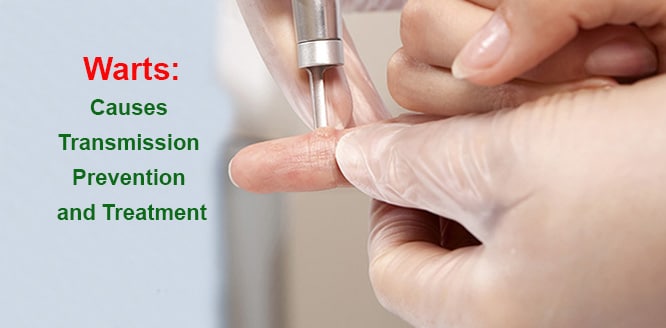
Warts are small, hard, swollen wound and acnes that occurred on the skin surface caused by the human papillomavirus. Although they are often harmless and painless, the appearance is disturbing. They can be seen on all over the body. But, they occur on the hands, knees, and feet more often. Warts on the genital area are of a different type. They can be dangerous and must be treated. Most warts disappear spontaneously within 1-2 years without treatment. However, medical treatment is required if they are large, numerous, or on sensitive areas. Different methods are applied in the treatment such as salicylic acid, cryotherapy, duct tape, surgery or laser therapy.
Table of Contents
What are warts?
Warts are rough skin wounds. They can occur anywhere on the surface of the body skin. There may be visible dark spots in the centre resulting from clotted blood vessels. They are caused by human papillomaviruses (HPV). Some sexually transmitted HPV types cause cervical cancer and other genital cancers. The types of HPV causing skin warts are mostly harmless. (1)
A wart may occur in 2-6 months after an infection. It usually disappears. However, their appearance can be disturbing for many people.
Causes of warts
They are of a virus origin. They occur due to the transmission of viruses in the HPV (human papillomavirus) family, which also cause genital warts. HPV causes excessive and rapid growth of keratin, a hard protein in the upper layer of the skin. As a result, a rough bump raises on the skin surface.
Children and adolescents are at risk because their bodies may not be immune to virus. In addition, HIV (AIDS) patients and those undergoing transplantation should be more careful against the virus due to the weakened immune system.
Causes of genital warts
There are 30 to 40 HPV types affecting the genital organs. However, only a few causes genital warts. Unlike others, these HPV types are highly contagious and they are sexually transmitted. They are so contagious that about 65% of those having sexual act with a person with them are thought to get infected.
However, they do not occur in everybody getting infected with the virus. Any person who is sexually active is at risk of HPV, and yet the risk of developing genital wart due to HPV virus in some people is much higher. (2)
Risk factors of genital warts:
- Age <30
- Smoking
- A weak immune system
- History of child abuse
- Genetic transmission of HPV virus from an infected mother.
Causes of foot warts
They occur on the sole of the foot due to HPV infection. Small cuts on the foot, fractures, or some weak spots on the foot sole make it easier to get infected the virus. However, the type of HPV that causes foot warts is not very contagious. It is not transmitted through direct contact.
However, it occur in hot, humid environments. Walking barefoot around the swimming pool or dressing rooms may cause virus infection.
Transmission of warts
Genital warts are sexually transmitted. Skin warts, on the other hand, can be transmitted through close contact, although they are not very contagious. For example:
- Walking barefoot around public swimming pools
- Using towels or manicure tools such as nail scissors or nail files in common may increase the risk of getting infected.
Furthermore, in a study it was found that the rate of warts was 34% higher in people constantly dealing with meat, such as slaughterhouse workers or butchers.
A wart anywhere on your body may also infect other areas. The factors are:
- Scratching or biting a wart on the hand,
- Sucking fingers,
- Biting nails with warts around,
- Shaving face or leg.
Types of warts
There are five main types. Each type appears on a different part of the body and has a different appearance.
Common warts
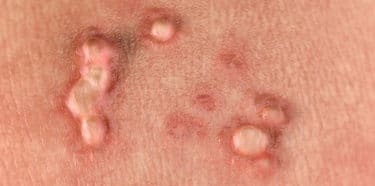
They appear on the hand and foot fingers, the skin around nails and backs of hands most often. It has a rough and protruding appearance. There may be black spots in the centre caused by capillary vessels.
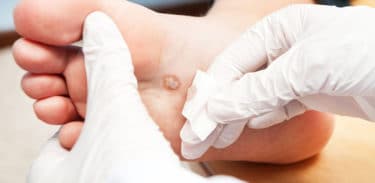
Foot (Plantar) warts
They often occur on the sole of the foot and heels. It grows into the skin due to the pressure by walking and standing. If you feel like there are small pebbles in your shoes, take a look at foot soles. They can sometimes be mistaken for calluses. If there are black dots on them, they might be warts. (3)
Flat warts
They often occur on the face, thighs, or arms. Their shape is like a flat hill with an abraded top. They are small and not easily noticeable. However, they’re in large numbers. Sometimes 20 to 100 flat warts can be seen on body of a person.
Filiform warts
They mostly occur around the eyes, mouth or nose, on the neck and under the chin. They grow very fast and have a spiky, eye-catching appearance, but they are painless. It is important not to touch them for the other parts of the body not to be infected.
Genital warts
They occur on the genitals and are sexually transmitted. They are very small, skin-coloured, or slightly darker than the skin. Therefore, it is difficult to see them with the naked eye. They can occur as a cluster or single. They may cause pain, vaginal discharge, bleeding, discomfort, or itching.
Genital warts are dangerous especially for women. Some types of HPV can cause cervical and vulva cancer. They must be treated.
Symptoms and diagnosis of warts
Often, they can easily be diagnosed by a dermatologist. The following symptoms may help diagnose: (4)
- Small, fleshy, rough, hard bumps,
- Skin-coloured, white, pink, or brownish
- Black dots with clotted blood vessels in the centre.
If the doctor is suspicious of a formation other than a wart, a biopsy may be required.
You should consult a doctor if they are painful, with changing colour and shape, do not respond to treatment, spread or recur, have an irritating size, or are large in number.
Treatment of warts
Sometimes they can heal spontaneously in 1-2 years or with simple home treatment methods. However, there is always a risk of recurrence. If they are disturbing due to the appearance or location, or are painful, there are some treatment methods that can be performed under the supervision of a doctor.
Treatment aims to stimulate the immune system to eliminate the wart and fight the virus. Preferred methods may vary depending on the location of warts, symptoms, and patient preferences. Treatment can take weeks or even months. Unfortunately, they can recur after the treatment. (5) The methods applied are as follows:
Salicylic acid
These are prescription or over-the-counter medicines that are applied directly on the wart. It can be found in liquid, gel, or tape forms. It cleans them by removing layer by layer. It may be more effective in combination with cryotherapy (freezing treatment).
Apply the medication after taking a bath as the warts are softened and you clean the upper part of the wart with a nail file or bath brick. Repeat this process once or twice a day for 12 weeks. To prevent recurring of warts, you can maintain the treatment for even 1 or 2 more weeks after the elimination of them.
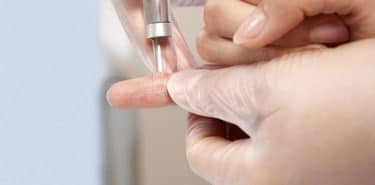
Freezing treatment (cryotherapy) for warts
Liquid nitrogen is applied to or sprayed on a wart by a specialist. Freezing process causes formation of water under and around wart. Dead tissue is removed within a week. It may be necessary to repeat method every 2-3 weeks, in three or four sessions in total. Pain, blisters, and skin discoloration may be seen in area of treatment after the process. After the skin heals, applying salicylic acid to the skin for more peeling may support treatment.
Studies show that cryotherapy is effective especially for hand warts. It is not recommended for young children as it is a painful procedure.
Wart tape (Duck tape)
In a study, treatment with a duct tape was found to be 45% more effective than cryotherapy. For this application, prefer transparent, but not silver duct tapes.
Apply the duct tape on your wart and wait 6 days. After removing the tape, wet the warts and file them. Leave it uncovered overnight and apply the tape again in the morning. Wait 6 days again. Repeat this application for 2 months or until the wart is eliminated. You can apply salicylic acid before applying the duct tape again.
Wart surgery
The technical name of the surgical treatment performed in warts is electrodesiccation and curettage. Local anesthesia is administered to the area, the doctor dries the wart with an electric needle and scraps with a spoon-shaped instrument called curette.
Scars may remain after this procedure. It is preferred if the wart does not respond to any other treatment. It should not be applied to warts on the soles of the feet.
Laser treatment for warts
In laser treatment, small blood vessels are burned with a laser. The tissue eventually dies and the wart is eliminated. Evidence for the effectiveness of this method is limited. It can also cause pain and scarring.
Wart creams
- Topical oinments, such as salicylic acid, tretinoine, and glycolic acid, allow the layers to peel off
- Immune stimulating oinments containing imiquimod (Aldara) and diphencyprone can help the warts get smaller and disappear.
- Topical 5-fluorouracil is a cancer medicine that prevents the growth of tumors. It prevents the growth of extra cells that cause warts.
What kind of doctor removes warts?
You can apply to the Dermatology Clinic of any health institution for treatment. A dermatologist can help you with the treatment.