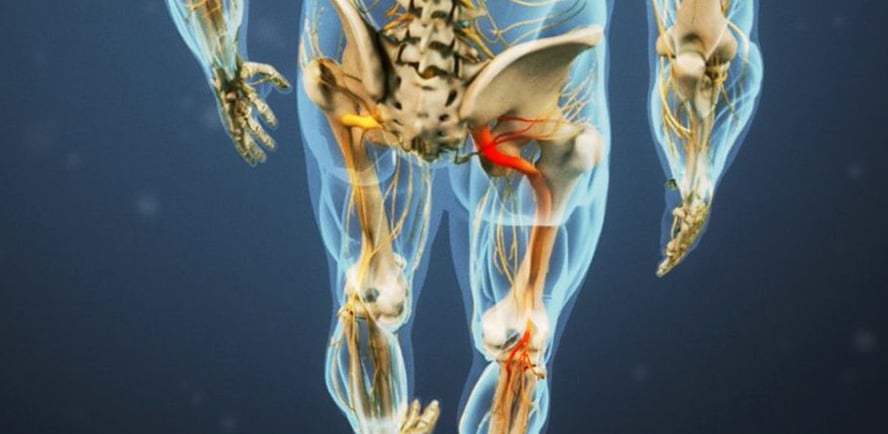
Sciatica pain is pain caused by compression or irritation of the sciatic nerve which is the longest nerve in the body extending from the waist to the back of the legs. It can cause pain, tingling, numbness or loss of strength in the legs. Although it is often confused with low back pain, sciatica pain is the pain extending downward on one leg. Health problems such as herniated disc, spinal stenosis, degenerative disc disease and spondylolisthesis can cause sciatica pain. Most cases can be treated with non-operative treatment approaches within 1-2 weeks. However, if a patient begins to have difficulty in bowel and bladder control and a decrease in leg strength, surgical intervention may be required.
Table of Contents
Causes of sciatica pain
The sciatic nerve is the longest nerve in the body. It starts from the bottom of the back through the hip and the legs on both sides and extends to the feet. When some health problems such as herniated disc put pressure on the nerve, an annoying pain occurs spreading from your waist to your hips and legs. Medical problems causing sciatica pain are as follows: (1)
- Herniated disc: The most common cause of sciatic pain (90%) is herniated disc. Herniated disc may cause pain directly compressing the spinal nerve root that forms the sciatic nerve. In addition, sometimes an acidic chemical may leak from the disc and this leakage may cause inflammation and irritation around the sciatic nerve.
- Lumbar spinal stenosis: Spinal stenosis is the narrowing of the spinal canal (the spinal cord in the lower back). It is more common over the age of 60.
- Spondylolisthesis (Waist dislocation): Sometimes vertebra slides slips onto another one due to a small stress fracture or a severe trauma. This compresses the sciatic nerve, thereby causing pain. Spondylolisthesis can also be congenital.
- Degenerative disc disease: Discs that act as pillows between the vertebrae wear out due to aging and lose their protective characteristics. As a result, they may compress or irritate the sciatic nerve.
- Cauda equina syndrome: It is a rare condition that usually requires emergency surgical intervention. It affects the nerves in the lower part of the spinal cord. It may lead to fecal or urine incontinence or permanent paralysis of the legs.
- Piriformis syndrome: It is caused by involuntary contraction of the piriformis muscle that connects the lower part of the spine to the femurs. Piriformis syndrome can put pressure on the sciatic nerve and cause pain. It is a rare condition.
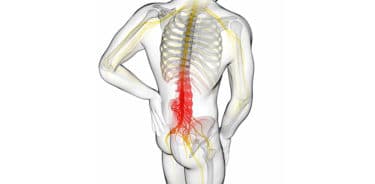
Other causes of sciatic pain:
- Tumors in the spine
- Infection affecting the spine
- Muscle spasm in the back or hips
- Injuries of the spine
- Pregnancy
- Overweight
- Not doing exercise regulary,
- Sleeping in a too hard or soft bed
- Wearing high-heels
Location of sciatic pain
Sciatica pain firstly occurs in the waist and spreads through hips to the back of left or right leg depending on the affected nerve. The pain may spread to the feet or toes depending on which part of the sciatic nerve is affected. In most cases, the pain occurs in one side of the body. (2)
Symptoms of sciatica pain
Sciatica Pain;
- May be mild or unbearable in severity.
- May prevent lifting your feet up.
- Worsen by coughing or sneezing.
- May sometimes be felt like electric shock.
- May exacerbate after sitting for a long while.
- Is felt only in one side of the body.
Sometimes, burning, numbness, tingling or muscle weakness may occur in the affected leg. There is also a risk of exacerbation when the pain is not too severe. Therefore, it may be good to take early measures by consulting a specialist.
Diagnosis of sciatica pain
The methods applied to identify the factors causing sciatica pain are as follows: (3)
- Physical examination: A doctor firstly asks questions about the type of the pain and the severity of it. S/he may also learn about your lifestyle. Then, s/he performs a physical examination including some exercises and movements to identify the nerve causing the pain. S/he also tests your muscle strength and reflexes with this examination.
- Imaging tests: If the pain is sever or chronic, some imaging tests such as X-ray, BT scan or MRI may be required. A herniated disc or bone growth which may cause sciatic pain can be diagnosed via theses tests. Moreover, an electromyography (EMG) may help identify which nerves are compressed.
How to relieve sciatica pain?
Sciatica pain can be treated with some simple implementations, which you can do at home, instructed by your doctor after being diagnosed with sciatica. Some implementations which can heal the pain are:
- Movement: Continue with your daily activities as much as possible. Inactivity may worsen your condition.
- Exercising regularly: Walking and stretching exercises which you can learn about from a physiotherapist may help alleviate the pain. You can also take yoga classes.
- Cold application: Wrap a package of ice (you can also use frozen vegetables) with a towel and apply it to the site of pain several times a day in the first few days of the pain. This application may alleviate inflammation and pain.
- Hot application: After 2-3 days of ice application, apply hot water a few times a day using a hot water bag. If the pain persist, you can alternate between cold and hot application.
- Alternative treatments: You can also use alternative treatments such as massage, biofeedback and acupuncture to control sciatic pain.
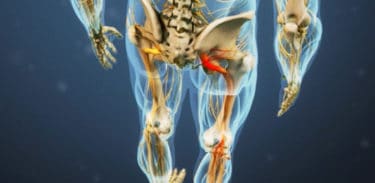
Treatment of sciatica pain
If sciatica pain exacerbates and does not heal spontaneously, there may be necessary to administer additional treatments under the supervisiob of a doctor.
Medicines for sciatica pain
Prescription and OTC painkillers which can be taken to alleviate sciatic pain are as follows: (4)
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): ibuprofen, aspirin, naproxen
- Oral steroids: Prednisone
- Anticonvulsants (antiseizure drugs): Gabapentin
- Tricyclic antidepressants: Amitriptyline etc.
- Opioid analgesics: Tramadole, oxycodone
These medicines are usually prescribed to both alleviate pain and enable patients to comply with physiotherapy. Medicines which may lead to drug dependency such as opioid analgesics are for short-term use.
Physiotherapy
You can get help from a physiotherapist when severe, acute pain is relieved. A regular physiotherapy program may help improve your posture, strengthen your back muscles, and increase your flexibility. (5)
Steroid injections
If the cause of sciatic pain is irritated nerve roots, corticosteroid is injected to the site of pain. Corticosteroids suppress the inflammation in this site and help alleviate tha pain felt. However, injections of corticosteroids are limited due to side effects. (6)
Chiropractic adjustment
The adjustment should be performed by a chiropractor. The aim of chiropractic adjusment, which is based on manual manipulation method of the body, is to align the spine. It can be performed in the treatment of conditions causing sciatic pain such as herniated disc or spinal stenosis.
Massage therapy
Massage therapy helps alleviate sciatica pain by regulating the bloodstream and relaxing muscles. It also increases the amount of endorphine which is natural painkiller secreted by the body
Surgical treatment
If none of the treatments administered relieve the pain, there is loss of bowel or bladder control, and the pain is not relieved despite the medicines administered, as the last resort, surgical treatment may be considered. There are two main surgical treatment methods:
- Discectomy: In this procedure, a surgeon excises the part of the disc compressing the sciatic nerve. However, sometime it may be necessary to excise all of the disc. Intervention is performed under general anesthesia and patients can be discharge on the same day.
- Laminectomy: Lamina is the back of the spine that covers the spinal cord. During the surgery, a surgeon removes the lamina and tissues compressing the sciatic nerve. It is performed under general anesthesia and may take about 2 hours.
How long sciatica pain last?
Sciatica pain may be acute or chronic. Acute pain gets over in 1-2 weeks. Drowsiness may be felt for a while after the pain is relieved. There is also the risk of recurrence. In some cases, acute sciatic pain can become chronic, that is, it becomes permanent. This is a problem lasting lifelong. However, it is usually less severe than acute pain.
Herbal treatment for sciatica pain
- Chamomile tea: Chamomile tea may help relieve sciatica pain with its muscle relaxant effect. You can drink 3 glasses a day.
- Epsom salt: Fill the tub with warm water. Add 1 cup of Epsom salt, 2 tablespoons of eucalyptus oil, and a few drops of lavender and chamomile oil. Rest for 20 minutes in the water. Repeat this every day until your pain is relieved.

Exercises for sciatica pain
Some basic exercises and stretching movements you can do at home may help alleviate your sciatica pain and regain your strength. When you do these exercises regularly every day, you will observe that the pain decreases within 2 weeks and completely disappears within 4-6 weeks.
Which doctor to consult for sciatica pain?
For sciatica pain, you can apply to the neurology or orthopedics department of any hospital. A physiotherapist can also help you through the treatment.