All types of acne are caused by clogging of the skin pores with too much oil, dead skin cells or bacteria. Inflamed acne is the transformation of this blockage into infection due to bacteria. This can be triggered by many factors, such as hormons, medications or wrong make-up products. Treatment is determined by the cause and severity of the acne. In mild cases, some basic treatment methods can be applied at home and over-the-counter medicines can be used. In severe cases, treatment with stronger prescription medicines is required. If the inflamed acne is not treated, it can cause a permanent scar or pockmark on the skin. The treatment must be be planned by a dermatologist.
Table of Contents
What is inflamed acne?
Inflamed acne is red swellings caused by pores deeply clogged with bacteria, oil, and dead skin cells. Although it is seen extensively on the face, back, chest, and shoulders, it can actually occur almost anywhere on the body. Non-inflammatory acne, also called comedonal acne, is closer to the surface of the skin and doesn’t have a bacterial basis.
Inflamed acne is highly normal unless they are severe enough to disrupt everyday life. Yet, if it is not treated, there is a high probability of leaving scars or pockmarks on the skin. Severe cases must be treated under the supervision of a doctor. (1)
Types of inflamed acne
The type of inflamed acne must be correctly identified to administer a correct treatment. The main types of inflamed acne with a severity ranging from mild to severe are:
- Papules: They are small, pink, and raised swellings that appear on the surface of the skin. It has neither white nor black visible center.
- Pustules: They are large and delicate bumps with an apparent circular center. Its base is pink or red, and there is white-yellow pus consisting of dead skin cells and bacteria in its center. They look like white dots, but they are larger.
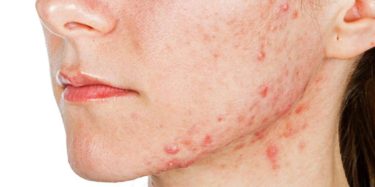
- Nodules: They are hard, painful, inflamed bumps that do not have an apparent center or head. They are formed under the skin surface and are filled with pus. Nodules are formed when the clogging in the pores damages the tissues beneath the skin surface. They can cause complications such as dark spots or scars on the skin.
- Cysts: Cysts are the most severe type of inflamed acne. They are large, soft, painful, red or white swellings that occur deep inside skin. They’re filled with pus and they are painful. Like nodules, complications such as scars and spots can develop on skin.
Causes of inflamed acne
How does inflamed acne occur?
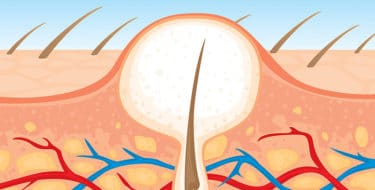
Sebaceous glands are small glands that produce an oily substance (sebum) that prevents the hair and skin from drying out. They are located close to the surface of the skin. These glands are attached to hair follicles, which are small pores from which the hairs come out.
When sebaceous glands begin to produce too much sebum, this sebum mixes with dead skin cells and clogs the pore. If the clogged pore is close to the skin surface, it will swell out, forming a white or black head. Harmless bacteria living on the skin can infect clogged pores and cause inflamed acne. (2)
Why does inflamed acne occur?
Acnes, formed due to any reason, may later turn into inflamed acnes as a result of bacterial contact. Factors that trigger acne formation:
- Testosterone: Sebaceous glands are sensitive to hormones. Especially, it is thought that puberty acne is triggered by testosterone hormone increased during this period. When the hormone level increases, sebaceous glands begin to produce excess sebum, which increases acne formation.
- Genetic factors: If acne is seen during adolescence or adulthood in one or both parents, the probability of occurrence in the child increases.
- Changes in hormone levels in women: Conditions that cause changes in hormone levels such as menstrual periods, pregnancy or polycystic ovarian syndrome, may increase the risk of acne in women.
- Some cosmetic products
- Some medicines: Steroid medicines, lithium, and some epilepsy medicines
- Some clothes or backpacks that irritate the skin
- Smoking
Inflamed acne treatment
If it is not treated, inflamed acne can spread and eventually cause scar, so it’s very important to start a treatment as soon as possible. Acne treatment should be followed by a dermatologist, regardless of the method applied. (3)
The main treatment methods:
Over-the-counter acne medicines
Dermatologist might suggest starting over-the-counter medicines before moving on to stronger prescription medicines. The over-the-counter products on the market used in the treatment of inflamed acne are:
- Benzoyl peroxide: This component may be suitable for fighting acne-causing bacteria. It can also prevent the formation of spots by drying the skin.
- Salicylic acid: This compound allows pulling dead skin cells and other debris out from the pores to the surface. It also prevents recurrence of inflamed acne lesions. It can be used all over your skin; however, due to its drying effect, it should be supplemented with a strong moisturizer.
It may take a few months to observe a difference. However, if there is still no change after 3 months, you may need to change your treatment and switch to stronger prescription medications. Therefore, you should consult a dermatologist.
Prescription acne medicines
- Topical retinoids: Retinoids are powerful, synthetic derivatives of vitamin-A, and help remove dead skin cells. Even though they might be included in some over-the-counter anti-aging products, prescription retinoids are effective for inflamed acne treatment. It may have side effects such as redness of the skin, peeling, and sensitivity to UV rays. Thus, it is necessary to use a protective sunscreen while taking the medicine. (4)
- Isotretinoin: Isotretinoin is one of the most powerful medicines used to treat inflamed acne. Due to the excessive side effects, it is usually prescribed in severe cases which do not respond to retinoid therapy like inflammatory cystic acne. Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding periods is strictly prohibited. (5)
- Oral antibiotics: If inflamed acne is caused by a bacterial infection, it may be necessary to take antibiotics. Antibiotics are usually used temporarily in cases of widespread cystic acne.
- Topical antibiotics: They can be used in a longer period than oral antibiotics. However, they are preferred in less severe cases of inflamed acne such as nodules, pustules or papules, as they are not too strong. (6)
- Hormonal treatments: In cases of inflamed acne due to hormonal imbalances, it may be necessary to take hormone-reducing medications. Birth control pills may be useful for women who have inflamed acnes before and during their menstrual cycles. Spironolactone, an anti-androgen medicine, may also treat nodules and cystic acne caused by unusually high androgen levels. (7)
Home remedies for inflamed acne
How to stop inflamed acne?
If acne is mild, such as papules or pustules, some medical practice that can be applied at home can also support treatment. For example:
- Wash the area with acnes with cold water and soap twice a day. However, make sure that your hands and the towel or cloth you are drying are clean.
- Always use an oil-free moisturizer after cleaning routine. If you do not do this, natural oil and water on your skin may deplete. Otherwise, sebaceous glands will produce more oil to balance, which leads to more acne.
- To open the pores, apply a warm compress with a sterile cloth to the area with acnes for 10 to 15 minutes.
- If you wear make-up, choose oil-free and non-comedogenic products that won’t clog your pores.
- Remove your makeup completely before washing your face at night.
Is inflamed acne squeezed?
As the hygienic conditions required to squeeze acne in the home environment are not met, they often cause undesirable results. Trying to squeeze cystic acne or acnes that are not particularly close to the skin surface can cause bacteria and other harmful substances to infect inner layers of the skin. As a result, acne may take longer to heal, and permanent scars may occur on skin.




With acne-prone skin, it is important to start with a free derma consultation scottsdale az to troubleshoot your skin, uncover hidden acne triggers, and customize the perfect skincare regimen for you.