Bone fracture is a condition where bone breaks down due to an accident, injury or excessive force. The bones break when they cannot resist a force or trauma applied to them. The first step in treatment success and rapid recovery is first aid and correct intervention to fractures. The correct diagnosis of the reason, type and location of bone fracture is second step of effective treatment and is very important for success of treatment. This is followed by selection of right treatment method according to type of fracture and the following of a good care process. Bone fractures are sometimes easily treated with plaster cast, whereas in more severe cases surgical intervention may be required. Today, there are many medical and surgical new treatment methods that can accelerate the healing process.
Table of Contents
How is a bone fracture diagnosed?
In the process of diagnosis of bone fractures, the physician first performs a physical examination, identifies symptoms and diagnoses the symptoms. The physician discusses about the circumstances that cause injury with the patient – or the patient is unable to communicate properly – with friends, relatives or witnesses. The next stage usually requires X-rays.
X-rays give a picture of internal tissues, bones and organs. Most fractures are diagnosed by an x-ray. Sometimes the fracture may not be visible in x-ray. This is especially common in some wrist fractures, hip fractures (especially older people) and stress fractures. In such cases, your doctor may require tests such as CT scan, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or bone scanning.
Sometimes, even after a bone fracture has been diagnosed, other tests (such as CT scan, MR or angiography, a special x-ray film of the vessels) may be needed to determine if other tissues around the bone have been damaged.
Bone fracture treatment
As the bone heals spontaneously in bone fractures, medical intervention and treatment focuses on supporting the bone and at the same time providing best conditions to injured bone for optimal healing (immobilization). The basic rule is that broken parts are reinserted and fixed so that they do not move until they are healed. This process is called “reduction”. Repositioning the bone without surgery is “closed reduction”. Most fractures are treated with closed reduction.
In severe fractures, open reduction may be necessary. In some cases, materials such as pins, plates, screws, rods or tissue adhesive are used to secure the bones. Open would and fractures should be thoroughly cleaned to avoid infection. Painkillers are used for pain relief or antibiotics can be used to prevent infection in open fractures. Even if the fracture is in plaster, rehabilitation begins as soon as possible. This treatment accelerates healing by regulating blood flow, protecting muscle tissue and preventing blood clots and stiffness.
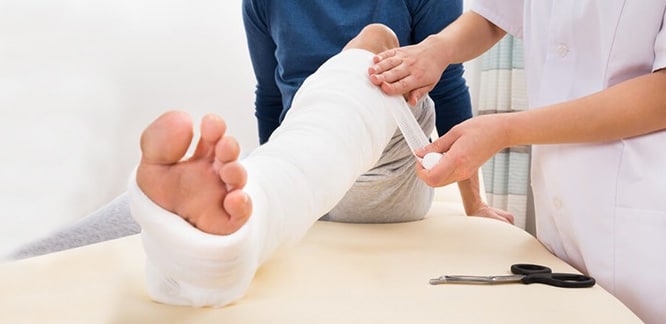
Best practice in the treatment of bone fractures
Immobilization
Fixing with splint and wrap
The fracture area is usually fixed using a soft filler, plaster material (gypsum, fiberglass) and ace bandage. This splint does not encircle the fracture, such as plaster cast, because there is a possibility of swelling of the tissues in the fracture environment over time, and if a tight plaster is made, swelling can cause many complications, including significant pain and potential blood circulation problems.
Therefore, the patient should be regularly placed icepack on the fracture site to help reduce swelling and inflammation after discharge. A few days later, when the swelling decreases, the splint can be replaced by plaster cast.
Plaster cast fixation
The most widely used material in fracture treatment are gypsum or fiberglass fixators. Because most fractures can only be healed after repositioning, and the bones are fixed with plaster to keep them in the proper position as the broken ends are healed.
Handy plaster cast or splint
In some cases, plaster or splint allows limited or controlled movement of nearby joints. This treatment is not desired in all fractures but desired in some fractures.
Traction
Traction is often used to align a bone or bones with a soft, continuous pulling motion.
External fixation
In this type of operation, metal pins or screws are placed into the broken bone above and below the fracture site. The pins or screws are connected to a metal rod outside the skin. This device is a stabilizing frame that holds the bones in the proper position as the bone tissue heals. Usually the bone area is fixed for 2-8 weeks.
The duration depends on which bone is affected, whether there are complications such as blood circulation problem or infection. In more severe cases, it may be necessary to wait up to 1 year. In case of damage to other soft tissues around the skin and fracture, an external fixator may be applied until the operation is tolerated.
Open reduction and internal fixation
During this process, bone fragments are first repositioned in their normal alignment, and then special screws or metal plates are attached to the outer surface of the bone. Particles can also be retained by inserting rods through the bone marrow in the center of the bone.
Bone fracture surgery
Surgical intervention may sometimes be required to treat a fracture. The type of treatment required depends on whether the fracture is “open” or “closed” or the location and severity. For example, a broken bone of the spine is treated differently from a broken leg bone or a broken hip. Internal and external rods and / or pins may be used to align and hold the bone in place.
Hip fractures almost always require surgery because other treatments are inadequate to ensure that the hip is kept still for a long time and usually results in poor outcome.
Bone fracture healing process
The bone heals in three stages.
- Reactive stage: The bruising occurs when the cells that will repair the fracture are collected in the fracture site. Known as a sign of gangrene, the bruise is actually a sign of recovery. In this process, the signaling molecules that provide intercellular communication begin to be released and the cells that produce bone (osteoblast) and cartilage producing (chondroblast) occur in the environment. Over the next few weeks, osteoblasts and chondroblasts have been busy producing bone tissue, while osteoclasts (bone cells) cleans bone waste in the region.
- Repair phase: This phase starts approximately 2 weeks after fracture formation. At this stage, the proteins produced by osteoblasts and chondroblasts begin to harden by the calcium mineral collapse and the structure called the soft callus, which is responsible for fixing the fracture, develops. The newly formed soft callus tissue hardens in the range of 6-12 weeks and turns into a hard callus that can carry loads. Physicians’ saying “bone is healed” actually means that hard callus is formed.
- The phase of redevelopment: This phase is the phase of reconstruction (remodelling) that is necessary for the bone to be restored and continues for months. In next few years, body will try to transform this mass into its original size and shape.
The healing process is usually simple if a broken bone is properly aligned and held still. The patient’s age, type of fracture, and general health of the patient are effective factors in how quickly the bone heals.
What adversely affects fracture healing?
- Radiation
- Tumor
- Mechanical imbalance
- Infection
- Corticosteroids
- Diabetes
- Smoking
- Chemotherapy
- Poor nutrition
- Metabolic bone disease
- Open fracture
Physical therapy in bone fracture
Broken bones knit at the earliest 6 weeks. In this process, movements that will lead to the recurrence of the fracture should be avoided. The physical therapy process in fractures is covered in two periods: during and after immobilization
During immobilization, massage-like physical therapy techniques are applied to reduce edema and pain. It is also taught to use aids such as crutches and canes. All of these treatment methods are very important in terms of accelerating the healing process after the removal of the fixative material.
Once the bone is healed, it is important to reduce the edema in the affected area and to increase muscle strength as well as to add to the insertion force. Rehabilitation devices used to accelerate the healing process in the physical therapy after the fracture and to help the muscles to strengthen at the moment are the devices such as magnetic field therapy, laser, ultrasound, compex electrical stimulation, fluidotherapy, Tens.
In the physical treatment process after the fracture, rehabilitation exercises applied by the physiotherapists with these devices complete the treatment. With these exercises, muscle weakness, pain, edema, shortens of muscles, and joint stiffness are prevented.
New approaches in the treatment of bone fractures
In the last decade, many technological developments and new medical and surgical techniques and approaches have been used in treatment of fractures. The goal here is to ensure that patients continue their work and social lives as soon as they get their health.
Functional immobilization
Contrary to the very heavy and long-cast gypsum material, the plaster used in this method is short, some parts are flexible-some parts are hard which is a plaster made of plastic material. This material allows the muscles to contract in gypsum area, thereby accelerating blood circulation in area and shortening the healing process of the fracture.
In most cases, individuals can walk on plaster. New type of plasters do not irritate the skin and are not allergic. The patient can bathe or even swim with this technique.
Bone marrow aspirate method (BMA)
In this method, the necessary material is obtained from the bone marrow. The bone marrow is removed by inserting a thick needle into the pelvic bone of the patient under operating conditions. It is difficult to apply but is more functional in the treatment because of the excess of stem cells it contains. This method is used in fracture healing as well as in some orthopedic disorders.
Platelet-rich plasma method (PRP)
The PRP method, which has been used in recent years, has been used for both non-healing fracture treatment and for different orthopedic disorders. In this method, approximately 20-30 cc of blood taken from the patient is subjected to a special process and the platelets, growth factors, in other words healing cells, are concentrated and separated. The approximately 5 cc fluid obtained at the end of this procedure is injected into the area of fracture healing or where there is intra-articular fracture.
Ultrasound treatment of bone fractures
It was found that daily low intensity ultrasound applied to the affected area helped to heal the fracture. Generally, it is a preferred treatment for stress fractures and small bone fractures. When applied to the right fractures, it accelerates the healing process by 50%. The application period is an average of half an hour each day.
Because it is an expensive treatment method, it is mostly preferred in professional athletes or in fractures that healing process will take for a long time.
Closed fracture fixation methods
These are the techniques done with small incisions of 2-3 cm without open surgery to the fracture area and shortens the healing time of the fracture. The nails are inserted into the bone from these few centimeters of incisions and these nails stabilize the broken bone extremely successfully.
Open surgery to the fracture area has some disadvantages. For example, blood vessels reaching the fracture site are very important in fracture and wound healing. In open operations, the intervention to these blood vessels may have a negative effect on recovery. Coagulated blood, which helps wrinkle around the fracture, is discharged during surgery. The risk of infection is higher. There is more pain in open surgery.
For all these reasons, if surgical intervention is required, closed surgery should be preferred. However, due to the necessity and technical difficulty of special and expensive operating room equipment such as scopy and fracture table, there may be disadvantages such as having to be done by a doctor specialized in this field.
Treatment of bone fractures in children
It is even more important to treat the fracture in children by using a closed fracture treatment. Growth cartilages in children are still functioning, and open fracture surgery can damage growth cartilages. Attention to open wounds and stitches after open surgery can create extra stress in the child and may limit his / her daily life.
Closed treatment of fractures of the child is done with scopy device (immediate x-ray imaging) in the operating room environment. The fracture fixation should be done by experienced specialists in the field of Pediatric Orthopedics with the help of special wires placed outside. No sore or suture.
Arthroscopy for joint fractures
It is a closed operation type applied in joint fractures. In the classical surgical method for fracture detection, joint is opened and direct vision is provided. This may cause joint stiffness. However, in modern approach, intraarticular fracture can be monitored from the monitor with the help of arthroscopy and it can be detected from the outside.
In this way, joint stiffness can be prevented as a result of open surgery, pain is much less and rehabilitation is provided very quickly. In addition, these operations are painless, the risk of infection is very small and the probability of good results is high.
Denture surgery for fracture treatment
With the partial hip replacement surgery performed in the hip fractures in the elderly, the patient is able to stand up and walk immediately after the surgery. Thus, the risk of complications such as heart-lung problems, urea elevation, and embolism, which develops as a result of prolonged restless sleep in the elderly and often result in death, is reduced.
Nowadays, thanks to developing techniques, prosthesis surgery can be easily applied to almost all hip fractures. A very important issue is that there is no age limit in operations.
Patients are often operated with spinal and epidural anesthesia without anesthetic anesthesia. Prosthetic surgery can be expensive compared to other treatment methods and requires a very good sterilization operating room environment. Blood thinners and anti-embolic socks are required to minimize the risk of embolism before and after surgery.
Ligament injuries and fractures
In the past, ligament injuries were not taken seriously and untreated during fracture treatments. Nowadays, it is known that ligament injuries are as important as fractures. Ligament injuries with or without joint fractures lead to serious problems such as deterioration of joint stability or calcification at very early ages if not treated. In particular, joint injuries with fractures can be overlooked and cause serious problems.
Early post-operative and immediate physical therapy
With the new applied methods and techniques, the operated limb and joint can be moved immediately. At the same time, physical therapy is started after fracture healing and physical therapy is started immediately after the new technique. Thus, patients gain muscle strength in a short time and return to their daily lives and athletic lives.