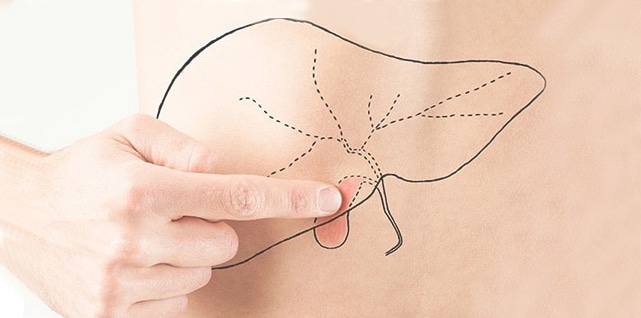
The gallbladder is an important organ that we remember when we get pain at the left side of our stomach. Major problems causing gall bladder pain are gallstones, inflammation of the gallbladder, inflammation of the pancreas, and inflammation of the biliary tract. Gallbladder pain used to describe any pain associated with gallbladder is a term that covers every reason associated with this organ. Symptoms and causes can be varied, can be triggered even with certain foods. Gallbladder pain can be very severe sometimes. In connection with its cause, it can be defined as the pain that is spread out to the back and remains constant in the abdomen. Research shows that women may be twice as likely to experience gallbladder disorders compared to men. Treatment of gallbladder diseases varies according to the cause of the disease.
Table of Contents
What is the gallbladder?
The gallbladder is a small pear-shaped sac located just below the liver and stores the bile produced by the liver. Bile is a fluid that helps the liver digest fatty foods. While the stomach and intestines digest food, the gallbladder purifies itself with a tube called the bile duct. The canal connects the gallbladder and liver to the small intestine.
Before meals, the gallbladder is as empty and flat as a collapsed balloon. After the meal, the gallbladder can be filled with bile to reach small pear size. If one of the bile ducts becomes blocked or inflamed by mud or gallstones, the person may experience pain.
Symptoms of gallbladder diseases
Gallstone and its symptoms
It is a painful disease caused by blockage of a canal from gallstones or sludge. It is also called uncomplicated gallstone disease. The pain usually becomes abrupt and in the upper abdomen, usually on the right side of the ribs, it also rises rapidly in the center and can spread to the right shoulder flank. It can occur anytime, either day or night, and pain episodes take about 1-5 hours; however, the pain duration is a few minutes.
The pain may be accompanied by nausea, vomiting and fever, and the pain can continue throughout the day, getting relieved every passing hour. There may be weeks and months between pain attacks or a pain. There may be pain attacks that would be like having a heart attack. If the pain is different from the new and other pains, the physician should be consulted. Eating fatty foods can sometimes trigger an attack.
Gallbladder inflammation (Acute cholecystitis) and its symptoms
This is the inflammation of the gallbladder tissue. Acute cholecystitis is usually caused by gallstones. But it can also be the result of tumors or other diseases. The pain is heavy and constant and lasts longer than pain in the gall bladder. It can occur in the right abdominal region and spread to the right shoulder. The pain can get worse with movement and coughing. Nausea, vomiting, fever, tremors and swelling can spread the pain to the abdomen.
Chronic cholecystitis and its symptoms
After a few episodes of acute cholecystitis, the gallbladder may shrink and lose its ability to retain and release bile. Abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting may occur. Chronic cholecystitis is usually treated with surgery.
Acalculous cholecystitis
Acalculous cholecystitis is still a gallbladder inflammation, but this time the disease has nothing to do with gallstone. Severe diseases such as severe physical trauma, heart surgery, or significant bacterial or viral diseases can trigger an attack. Symptoms are similar to acute cholecystitis with gallstones.
Multiple choledochus (choledocholithiasis)
Gallbladder stone occurs in gallbladder neck and bile ducts in multiple choledochal diseases. This may cause inflammation or swelling of the gallbladder. Disease manifested by severe pain in the middle of the upper abdomen can also be diagnosed by symptoms such as fever, chills, nausea, vomiting, hepatitis and clay colored feces.
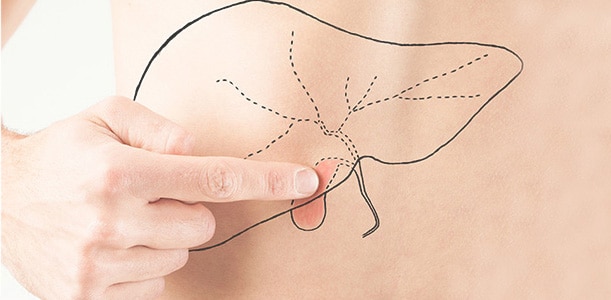
Gallbladder dyskinesia symptoms
Gallbladder dyskinesia occurs when the gall bladder runs less than normal. This condition may be related to ongoing gallbladder inflammation. Symptoms include post-meal upper abdominal pain, nausea, bloating and indigestion. Eating fatty foods can trigger symptoms. If there is biliary dyskinesia in the gallbladder, there is usually no gallstones. To help diagnose this condition, your doctor may recommend a test called HIDA screening. This test measures the function of the gallbladder.
Cholangitis and its symptoms
Cholangitis is the infection of the bile ducts. Initially, upper abdominal pain at right side may be accompanied by fever and chills, itching and hepatitis (yellowing of the eyes and skin) and may spread to the entire abdomen. This requires immediate medical treatment.
Especially if abdominal pain develops for more than eight hours, if there is no relief from the severity of the pain accompanied by high fever or chills, and if there is hepatitis in the eyes and skin, a doctor should be visited without delay and emergency services of hospitals should be visited according to situation.
Gallbladder cancer and its symptoms
Gallbladder cancer is rare. When diagnosed at an early stage, the chances of treatment success is very high. However, gallbladder cancer is difficult to diagnose because its symptoms are unclear. Therefore, the relatively hidden structure of gallbladder facilitates growth of gallbladder cancer without detection. Gallbladder cancer is usually manifested by pain, abdominal distension, fever, weight loss, nausea and hepatitis on skin and eye.
Diagnosis of gallbladder diseases
Abdominal ultrasound
It is a good technique especially for gallbladder stones and controls the gallbladder wall.
HIDA scan (Cholescintigraphy)
In HIDA screening, a radioactive chemical or tracer is injected through a vein in the arm. The monitor watches as the liver produces bile. A special nuclear medical scan tool (camera) follows the process of its flow from the liver to the gallbladder and then to the small intestine. This method has several side effects. These side effects are: an allergic reaction to radioactive tracers, bruising and itching at the injection site. Pregnant women or nursing mothers should report these conditions to the doctor.
Nuclear medicine tests, such as HIDA screening, mostly do not apply to pregnant women, as they have the potential to damage the fetus.
MR Cholangiography
Stone, obstruction, stenosis, tumor and biliary sludge can occur in bile and pancreatic pathway plays great role in diagnosis. This procedure is a method used only for interventional diagnosis. The dye is injected into the bloodstream, which focuses on the gallbladder and ducts and causes the problem to reveals in X-ray shots.
ERCP (Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangio Pancreatography)
If any health problems are detected in bile and pancreas pathways, treatment process is started with ERCP method. ERCP is safest method especially in cases of biliary stones and is considered as the first option for interventions to the biliary tract. A flexible tube is placed into small intestine from the stomach and dye is injected through the tube into the bile duct. The physician should be informed if an allergic reaction occurs prior to entering the imaging procedure. Although ERCP is generally safe, it has some side effects.
The most important of these is the inflammation of the pancreas, bleeding during the electrical incision and intestinal perforation. In general, these side effects can be eliminated by endoscopic intervention, however, surgical intervention may be required and inpatient treatment may be used. In addition, allergic reactions due to injected dye or health problems in the kidneys may be encountered; the possibility of encountering any side effects is very low in case the dye is not used.
Endoscopic ultrasound (Endosonography)
A small ultrasound probe at the end of a flexible tube is inserted into the intestines by mouth. This method can help diagnose bile duct stone and gallstone pancreatitis. Endoscopic ultrasound is not different from classical endoscopy. Similar side effects may occur. Since this procedure may last longer than normal endoscopy (about 30 minutes), the patient is given sedative and painkiller medication in order not to feel disturbance during the procedure.
Since the effect of these drugs may continue after the procedure, it is appropriate to have someone to accompany the patient. The physician should be informed about medications that are regularly used and the concomitant illnesses if there are any. When using the diagnostic method, serious complications such as bleeding and puncture, and the side effects related to the drugs used may be seen. The outpatients who come to the hospital for this procedure are usually sent to home after a few hours following the procedure and they can return to their normal daily routines the next day if there is no other problem.
Abdominal X-ray
Although it is used to detect other problems in the abdomen, X-rays cannot usually detect gall bladder disease, but they can detect gallstones.
Gallbladder problems are rarely fatal, and worsening of problems can easily be prevented if treated.
Treatment of gallbladder diseases
Gallbladder surgery (cholecystectomy)
Surgical intervention to remove the gallbladder is a treatment method usually used in painful gallstones or gallbladder cancer. There are two basic methods to remove the gallbladder:
- Laparoscopic (keyhole) cholecystectomy: A few small cuts are made to abdomen and thin surgical instruments are used to reach and remove the gallbladder. The effect of keyhole surgery is not long. Most patients can leave the hospital on the same day or the next morning and most likely return to most of the normal activities in two weeks.
- Open surgery: A single, larger incision is made to the abdomen to reach and remove the gallbladder. After open surgery, body takes longer to recover. You may need to stay in hospital for 3 to 5 days and may take six to eight weeks to return to normal.
Both techniques are performed under general anesthesia and no pain is felt.
Gallbladder extraction surgery is considered a safe procedure, but some complications such as wound infection, bile leakage into the abdomen, damage to the bile ducts, or blood clotting may occur.
Drug and antibiotic treatment
Gallbladder inflammation is primarily treated with pain medication. Because the pain is often severe, you may need to use prescription drugs. Your doctor may prescribe medications with codeine or hydrocodone. In some cases, more powerful painkillers such as morphine may be used. Non-prescription drugs such as ibuprofen and naproxen are often not preferred because they can cause nausea and vomiting.
In addition, infection may occur in cases such as acute cholecystitis. Although antibiotics do not typically treat cholecystitis, they can prevent infection to spread. There is also a treatment where chemicals are injected from the skin into the gallbladder by injecting a needle into the gallstones, but this method is rarely used.
Chemotherapy and radiotherapy
In gallbladder cancer, chemotherapy and radiotherapy can be used to prevent the return of cancer after surgery.
Ursodeoxycholic Acid
This is an oral medication option for gallstones in patients who are not eligible for surgery. This drug can help dissolve small cholesterol gallstones and reduce symptoms. Another oral solution is Chenix.
Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy
High-energy shock waves are reflected by breaking gallstones from a machine passing through abdominal wall. This method is effective if there are only a few small gallstones.
What causes Gallstones?
80 percent of gallstones are made of cholesterol and 20 percent of them are made of calcium salts and bilirubin. Although it is not known exactly, there are several factors in the formation of gallstones. There may be too much cholesterol in your gallbladder. If your liver produces more cholesterol than your gallbladder can disintegrate, yellow cholesterol stones can be composed in your gallbladder.
Excessive amounts of pigment called bilirubin can be found in your body. Bilirubin is a chemical produced when your liver destroys old red blood cells. Conditions such as liver damage and some blood disorders cause your liver to produce more bilirubin.
Pigment occurs when the gallbladder cannot disintegrate excessive bilirubin. These hard stones are usually dark brown or black. The gallbladder may not be completely or as empty as needed. The gallbladder must be drained of bile to ensure it is healthy and functioning properly. If the bile does not release its contents, the bile is intensely condensed, which causes stones to form.
What happens when gall bladder is removed?
There’s nothing to worry about. The absence of gall bladder does not adversely affect the body. You can sustain a normal life. The liver continues to produce bile to digest food, but instead of storing it in the gallbladder, it continually drips into the digestive tract. Although a special diet is recommended before surgery, there is no need to continue. A healthy and balanced diet should be targeted. Some patients may experience problems such as bloating or diarrhea after surgery, and this lasts approximately for several weeks.
Herbal treatment of gallbladder diseases
Studies have shown that the extract of camel thistle (150 mg twice a day) increases the bile flow and help to clear the liver and gall bladder due to its antioxidant properties.
- Lipase enzymes (two caps with food) support bile to digest fat
- Bile salts (500-1,000 milligrams with meals) can help break down fats and greatly reduce gallbladder discomfort
- Turmeric and its most active compound curcumin (1,000 mg per day), has anti-inflammatory properties; can help reduce gall bladder swelling and improve bile flow
- Dandelion is a plant that is very good for gallbladder. It is mainly consumed as tea and helps to expel the gallbladder stone. Experts recommend that this plant should be consumed regularly for three months in the mornings and evenings. During this period, it was observed that when consumed regularly, it disintigrated gallbladder stones.
- Barberry can fight with infections, purge the liver and gall bladder
- Mix three drops of rosemary oil with a quarter teaspoon of coconut oil and apply twice daily to the gallbladder area to reduce inflammation.
Prevention of gallbladder diseases
- Try to consume foods rich in fiber such as flax or chia seeds, raw almonds or raw nuts at least 30 to 40 grams per day
- Beet, artichoke and dandelion leaf are nutrients that help supporting liver health. You can produce your own vegetable juices by adding foods rich in potassium such as avocado, leafy greens, tomatoes, sweet potatoes and bananas.
- Protect your liver and gall bladder by using unrefined healthy fat such as olive oil or coconut oil.
- Feeding with fruits and vegetables reduces gallstone formation
- Fat-free organic protein sources in the gallbladder diet can reduce stress. Add lean protein foods such as organic chicken, turkey, beef and wild fish to your diet list.
What we should not eat?
- Avoid fried foods and hydrogenated fats. Fast food, processed oils, packaged meats or cheeses, chips, biscuits, salami-sausages, processed meats are some of the foods most difficult to digest due to the harmful oils they contain.
- Foods containing sugar and carbohydrates increase the risk of gallstones
- Gall bladder problems are potentially associated with food allergies. Carefully consume potential allergen foods such as dairy products, gluten, shellfish, peanuts
- Do not eat too greasy. Fatty foods may worsen gallbladder problems. But you can consume healthy fats such as olive oil or coconut oil.